Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are a common type of infection that affect millions of people each year. While they are more common in women, men can also develop UTIs. These infections occur when bacteria enter and multiply in the urinary tract, causing discomfort and sometimes serious complications if left untreated.
In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatments of UTIs, as well as steps you can take to prevent them from occurring. Whether you have experienced a UTI before or are simply interested in learning more, read on to discover important information about this common infection.
What Is Urinary Tract Infection?

Image from iStock
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are one of the most common infections that affect the urinary system, which includes the bladder, kidneys, urethra, and ureters. They are caused by the invasion and multiplication of bacteria in the urinary tract, leading to inflammation and discomfort. While UTIs are more common in women, men can also develop them.
What Causes UTI?
The most common cause of UTIs is when bacteria enter the urinary tract via the urethra and start to proliferate in the bladder. It is the purpose of the urinary system to keep bacteria out. Yet sometimes the defences fall apart. If that occurs, germs may establish a foothold and develop into a serious infection in the urinary system.
The bladder and urethra are the most commonly affected areas by UTIs, which mostly affect women.
- Infection of the bladder. Escherichia coli typically causes this type of UTI (E. coli).
E. coli is a prevalent type of bacterium in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. But occasionally, other microbes are to blame.
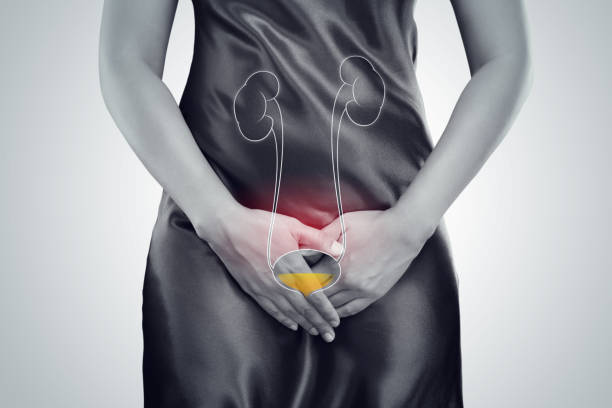
Image from iStock
Although you don’t have to be sexually active to get a bladder infection, having sex can certainly cause one. Due to the anatomy of women, they are all susceptible to bladder infections. The urethra is near the anus in females. Moreover, the bladder is close to the urethral entrance. This facilitates the entry of microorganisms around the anus into the urethra and subsequent passage to the bladder.
- Infection of the urethra. Anus to urethra transmission of GI bacteria can result in this kind of UTI. Sexually transmitted infections can also result in an infection of the urethra. These include mycoplasma, chlamydia, gonorrhoea, and herpes. Women’s urethras are located close to the vagina, which makes this possible.
UTI Symptoms
Not all UTIs result in symptoms. When they do, they could consist of:
- A persistently intense urge to urinate
- Urination that causes burning
- Often passing little volumes of pee when urinating
- Cloudy-looking urine
- Red, bright pink, or cola-coloured pee – indications of blood in the urine
- Urine that smells strongly
- Pelvic discomfort in women, particularly in the region of the pubic bone and the centre of the pelvic.
UTIs in older persons may go unnoticed or be confused with other illnesses.
Types of UTI
Different UTI types can cause different symptoms. Which portion of the urinary system is impacted determines the symptoms.
|
|---|
|
Part of urinary tract affected
|
Signs and symptoms
|
|
Kidneys
|
- Back or side pain
- High fever
- Shaking and chills
- Nausea
- Vomiting
|
|
Bladder
|
- Pelvic pressure
- Lower belly discomfort
- Frequent, painful urination
- Blood in urine
|
|
Urethra
|
- Burning with urination
- Discharge
|
Treatment For Urinary Tract Infection
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are typically treated with antibiotics, which are medications that are designed to kill the bacteria that cause the infection. The specific antibiotic that is prescribed will depend on the type of bacteria causing the UTI and the severity of the infection.
In addition to antibiotics, there are also some home remedies and lifestyle changes that can help to alleviate the symptoms of a UTI and speed up the healing process.
Here are some common treatments for UTIs:
1. Antibiotics
The most common treatment for UTIs is a course of antibiotics, which are usually taken for 3-7 days depending on the severity of the infection. Some of the antibiotics that may be prescribed include amoxicillin, ciprofloxacin, and nitrofurantoin.
2. Pain relievers
Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help to relieve the pain and discomfort associated with a UTI.
3. Drinking plenty of water

Image from iStock
Drinking lots of water can help to flush out bacteria from the urinary tract and speed up the healing process.
4. Urinate frequently
Urinating frequently helps to eliminate bacteria from the urinary tract and prevent them from multiplying.
5. Avoid irritants
Avoiding irritants such as caffeine, alcohol, and spicy foods can help to reduce the discomfort associated with Urinary Tract Infection.
6. Applying heat
Applying a heating pad or hot water bottle to the lower abdomen can help to alleviate pain and discomfort.
It is important to note that while home remedies and lifestyle changes can help to alleviate symptoms, antibiotics are usually necessary to fully treat a UTI. If you suspect that you have a UTI, it is important to seek medical attention promptly in order to receive an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Left untreated, UTIs can lead to serious complications such as kidney damage or sepsis.
How To Prevent UTI
The following precautions may help reduce the risk of UTIs:
1. Consume plenty of fluids, particularly water
Water helps to dilute the pee. This causes more frequent urination, allowing bacteria to be flushed from the urinary tract before an illness may develop.
2. Consider cranberry juice
The findings of studies exploring whether cranberry juice reduces UTIs are preliminary. Drinking cranberry juice, on the other hand, is unlikely to be harmful.
3. Wipe from the front to the back
Do this after urinating and after having a bowel movement. It aids in the prevention of bacteria spreading from the anus to the vagina and urethra.
4. Just after having sex, empty your bladder.
Drink a full glass of water as well to help flush bacteria.
5. Stay away from possibly irritating feminine products.
When used in the vaginal area, they can irritate the urethra. Deodorant sprays, douches, and powders are examples of these items.
6. Alter your method of birth control.
Diaphragms, unlubricated condoms, and spermicide-treated condoms can all contribute to bacterial growth.
If you experience symptoms of a Urinary Tract Infection, it is important to seek medical attention promptly. Left untreated, UTIs can lead to complications such as kidney damage or sepsis, which can be life-threatening.
In conclusion, UTIs are a common infection that affects the urinary system. While they can be uncomfortable and unpleasant, they are usually easily treated with antibiotics. By taking steps to prevent UTIs from occurring, such as practicing good hygiene and staying hydrated, you can reduce your risk of developing this infection.
Here at theAsianparent Singapore, it’s important for us to give information that is correct, significant, and timely. But this doesn’t serve as an alternative for medical advice or medical treatment. theAsianparent Singapore is not responsible for those that would choose to drink medicines based on information from our website. If you have any doubts, we recommend consulting your doctor for clearer information.
 Together Against RSV
Together Against RSV SG60
SG60 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Parenting
Parenting Child
Child Feeding & Nutrition
Feeding & Nutrition Education
Education Lifestyle
Lifestyle Events
Events Holiday Hub
Holiday Hub Aptamil
Aptamil TAP Recommends
TAP Recommends Shopping
Shopping Press Releases
Press Releases Project Sidekicks
Project Sidekicks Community
Community Advertise With Us
Advertise With Us Contact Us
Contact Us VIP
VIP Rewards
Rewards VIP Parents
VIP Parents
